Metalenses is a compound element with many different uses. It is also known by several other names, including colloidal gold, colloidal silver, and compressed air, in addition to many trade names. A thin film of metal extends the surface area of any piece, while adding a protective layer of metal or other material. The layers are usually obtained from a variety of alloys, with most often being a mixture of tin, copper, zinc, nickel, cobalt, and titanium.
The method has applications well beyond lens fabrication: for selective crystallization, laser ablation, and even annealed electron microscopy, for instance. However, it’s in chip fabrication where the technology has the greatest potential. Because of the high energy density which focuses on the optical waveform, metalenses of this type can potentially be used on next-generation nano-lithology with targeted focused beams for creating highly sensitive micro-fabrication devices. This will allow researchers to create micro-chips of a very small size, with very exact precision. By combining the metalenses with techniques such as cavity gas adiabatic electron microscopy, researchers will be able to create miniature versions of large-scale devices, such as electronics chips.
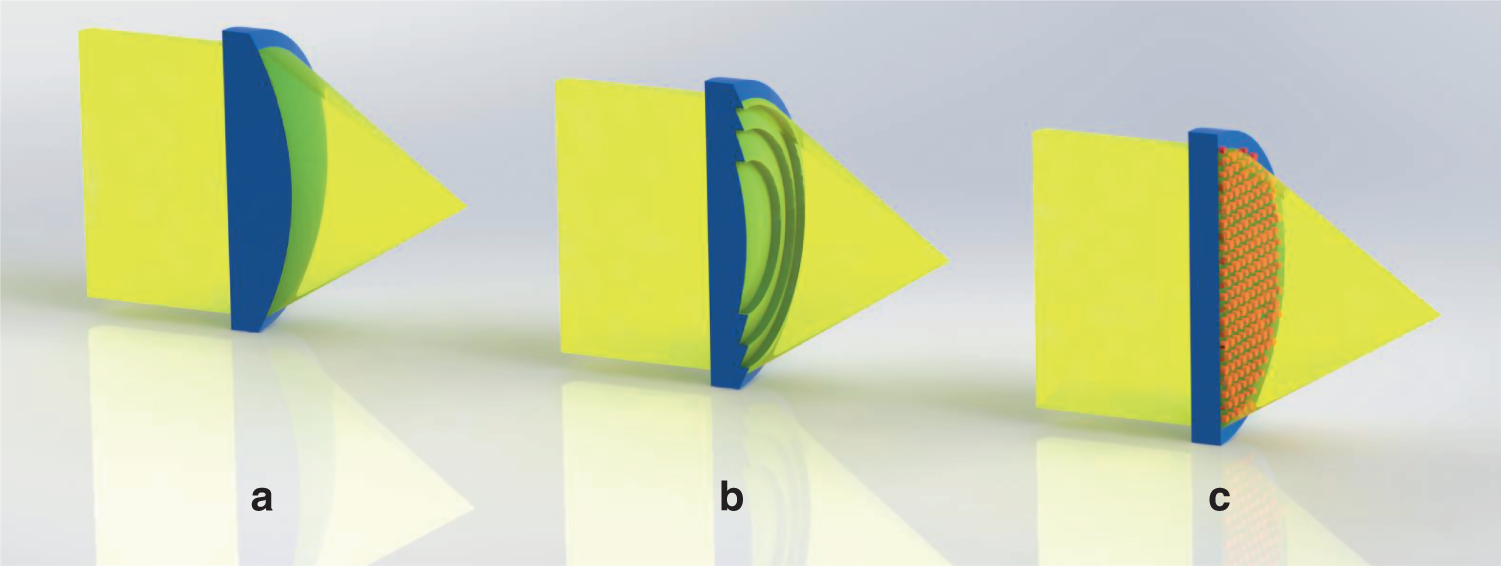
Metalenses come in a variety of forms. They can be shaped like flat disks or “walls” for focusing light, or they can be shaped more like honeycombs to focus light on a given area. The most common form used in optical devices today is a solid-state ring made out of metal. These rings are often designed to focus light in certain areas of a device, although their most common use is to focus the light on a very thin film, like a wafer of metal. The ring could also be made to focus light in a completely different direction, which is useful when you need to focus light in a non-luminous manner.
In terms of their physical makeup, metalenses are made out of one of two different materials. Either the surface is made up of an extremely hard material, or the material contains holes that are larger than the diameter of the lens. The holes in the material to allow waves to pass through the lenses, but prevent them from entering other mediums. The most commonly used medium is gases, because these allow the waves to travel through the lenses without being slowed down. Metalenses are a great alternative to traditional lenses because of their extreme ability to focus light.












